A Cocaine-Activated Ensemble Exerts Increased Control Over Behavior While Decreasing in Size
Thibeault et al., Biological Psychiatry, In press. 2025
Substance use disorder is characterized by long-lasting changes in reward-related brain regions, such as the nucleus accumbens. Previous work has shown that cocaine exposure induces plasticity in broad, genetically defined cell types in the nucleus accumbens; however, in response to a stimulus, only a small percentage of neurons are transcriptionally active—termed an ensemble. Here, we identify an Arc-expressing neuronal ensemble that has a unique trajectory of recruitment and causally controls drug self-administration after repeated, but not acute, cocaine exposure. Using Arc-CreERT2 transgenic mice, we expressed transgenes in Arc1 ensembles activated by cocaine exposure (either acute [1 3 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally] or repeated [10 3 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally]). Using genetic, optical, and physiological recording and manipulation strategies, we assessed the contribution of these ensembles to behaviors associated with substance use disorder. Repeated cocaine exposure reduced the size of the ensemble while simultaneously increasing its control over behavior. Neurons within the repeated cocaine ensemble were hyperexcitable, and their optogenetic excitation was sufficient for reinforcement. Finally, lesioning the repeated cocaine, but not the acute cocaine, ensemble blunted cocaine self-administration. Thus, repeated cocaine exposure reduced the size of the ensemble while simultaneously increasing its contributions to drug reinforcement. We showed that repeated, but not acute, cocaine exposure induced a physiologically distinct ensemble characterized by the expression of the immediate early gene Arc, which was uniquely capable of modulating reinforcement behavior.
Figure 1. Repeated cocaine exposure affects the trajectory of ensemble recruitment in an immediate early gene–dependent fashion.
(A) Schematic showing experimental groups tagged by Arc (TdTomato) and c-FOS. (B) (i) Representative images of tdTomato expression in the NAc core of Arc-CreERT2 3 Ai14 mice. Mice were injected with 4-OHT, opening a window during which Arc transcription resulted in tdTomato expression in the same cells. Transcriptionally active neurons were labeled following: (left) a saline injection, (middle) cocaine injection (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally), or (right) cocaine injection (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) following 10 days of repeated cocaine injections. (ii) Representative images of c-FOS–immunoreactive nuclei in the NAc core in the same ensembles: (left) saline injection, (middle) cocaine injection, or (right) cocaine injection (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) following 10 days of repeated cocaine injections. (C) Number of tdTomato-positive nuclei in NAc core— indicating neurons that expressed Arc during the tagging window—in the saline, acute cocaine, and repeated cocaine ensembles normalized to the number of neurons identified in the saline ensemble (1-sample t test: saline t9 = 0.00036, p = .99; acute cocaine t9 = 0.36, p = .73; repeated cocaine t6 = 8.27, p = .0002). (D) c-FOS1 nuclei normalized to the number of nuclei detected in the saline ensemble (1-sample t test: saline t3 = 8.54 3 1025, p . .99; acute cocaine t3 = 1.074, p = .36; repeated cocaine t3 = 5.90, p = .0097). (E) The change in the number of cells labeled with c-FOS or Arc for each treatment group normalized to the saline ensemble for each respective immediate early gene (2-way analysis of variance, interaction: F2,33 = 4.09, p = .026; 2-way analysis of variance, main effect immediate early gene: F1,33 = 11.75, p = .0016; Sidak’s test for c-FOS vs. Arc repeated cocaine: t33 = 3.93, p = .0012). Values indicate mean 6 SEM unless otherwise indicated. Data points in panels (C) and (D) represent individual animals. **p # .01, ***p # .001. AC, anterior commissure; NAc, nucleus accumbens.
Figure 2. The number of neurons activated by cocaine in vivo is reduced over repeated cocaine exposure.
(A) Schematic of the timeline of calcium imaging. Miniscope recordings were performed on the first day and the tenth day of cocaine (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) injections in the same animal. Calcium activity was recorded during a 5-minute baseline period (0–5 minutes), for 5 minutes after a saline injection (5–10 minutes), and for 10 minutes after a cocaine injection (10–20 minutes). An additional recording was collected 1 hour after the cocaine injection (60–65 minutes). (B) Representative maximum projection image for the field of view through the miniscope (yellow = excited, blue = inhibited, red = no change). (C) Representative traces showing different cellular responses to cocaine that we identified. One group of neurons was excited in response to cocaine injections (yellow); 1 group was inhibited in response to cocaine (blue); a third group showed no change (gray). (D) Heatmaps for cell activity (events/min) on day 1 and day 10. Cells were sorted according to activity following cocaine injection. (E) Venn diagram depicting cells that showed increased firing activity on day 1 in response to either cocaine or saline, where a significant minority of neurons showed increased activity to both injections. The numbers in the Venn diagram represent the number of cells. (F) Proportions of each activity phenotype observed after cocaine for each mouse (n = 5) on days 1 and 10. With repeated cocaine injections, more neurons were inhibited on day 10, and fewer neurons were excited on day 10 (inhibited c2 4 = 350.00, p , .0001; no change c2 4 = 32.86, p , .0001; excited c2 4 = 37.81, p , .0001). (G) Proportions of cells excited (yellow), inhibited (blue), or showed no change (gray) in activity after cocaine injection were significantly different on day 1 and day 10 (c2 2 = 28.97, p , .0001). Data points in panel (F) indicate individual animals. Values indicate mean 6 SEM unless otherwise indicated. ****p , .0001. GRIN, gradient-index; NAc, nucleus accumbens.
D1 and D2 medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens core have distinct and valence-independent roles in learning
Zachry, Kutlu et al., Neuron, In press, 2024
At the core of value-based learning is the nucleus accumbens (NAc). D1- and D2-receptor-containing medium spiny neurons (MSNs) in the NAc core are hypothesized to have opposing valence-based roles in behavior. Using optical imaging and manipulation approaches in mice, we show that neither D1 nor D2 MSNs signal valence. D1 MSN responses were evoked by stimuli regardless of valence or contingency. D2 MSNs were evoked by both cues and outcomes, were dynamically changed with learning, and tracked valence-free prediction error at the population and individual neuron level. Finally, D2 MSN responses to cues were necessary for associative learning. Thus, D1 and D2 MSNs work in tandem, rather than in opposition, by signaling specific properties of stimuli to control learning.
Figure 1. D1 and D2 MSNs do not track stimulus valence
(A) Cre-dependent GCaMP6f (AAV5.hsyn.flex.CGaMP6f) was expressed in D1 MSNs (D1-cre mice) or D2 (A2A-cre mice) MSNs. (Right) Example of GCaMP6f expression in NAc core.
(B) D1 MSNs showed a positive response to sucrose retrieval in a positive reinforcement operant task (two-tailed independent sample t test, t45 = 2.897, p = 0.0058, n = 5 mice). Dark gray dots are individual trials across all animals, light gray dots are averaged responses for each animal.
(C) D2 MSNs showed a decrease to sucrose retrieval in the same task (two-tailed independent sample t test, t60 = 6.29, p < 0.0001, n = 5 mice).
(D) D1 MSNs showed an intensity-dependent positive response to unsignaled shock (nested ANOVA, F(1,39) = 6.53, p = 0.016, n = 5 mice).
(E) D2 MSNs showed an intensity-dependent positive response to unsignaled shock (nested ANOVA, F(1,47) = 5.04, p = 0.031, n = 6 mice).
(F) Intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) task design. An excitatory opsin (ChR2; AAV5.Ef1a.DIO.hChR2) or a control vector (eYFP; AAV5.hSyn1.eYFP) was expressed in D1 MSNs or D2 MSNs in the NAc core. Nose pokes resulted in laser illumination (14 Hz, 2 s, 8 mW, 470 nM). Viral expression of ChR2 in the NAc core.
(G) Mice were trained to nose poke for optical stimulation of either D1 MSNs or D2 MSNs over 4 days.
(H) D1-Cre (D1 MSN) and A2A-Cre (D2 MSN) mice showed a preference for the active nose poke as compared with eYFP controls (repeated measures ANOVA, trial × group interaction F(6,42) = 3.17, p = 0.0118).
(I) D1-cre (n = 5 mice) and A2A-Cre (D2 MSNs, n = 7 mice) showed a greater percentage of total responses on the active operanda as compared with the eYFP controls (n = 5 mice, one-way ANOVA, F(2,14) = 8.96, p = 0.0031; Dunnett’s post-hoc eYFP versus D1, p = 0.036; eYFP versus D2, p = 0.0016).
(J) Training-dependent increase in responses in D1-Cre and A2A-Cre mice as compared with eYFP (one-way ANOVA, F(2,14) = 4.60, p = 0.0291; Dunnett’s post-hoc eYFP versus D1, p = 0.025; eYFP versus A2A, p = 0.049).
Data represented as mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Scale bars = 50 μm.
Figure 6. D2 MSNs, but not D1 MSNs, change dynamically over learning in both the pattern and timing of responses to learned cues
(A) Neural trajectories summarizing the activity of D1-MSNs in fear-conditioning session 1 (FC1, [i], n = 157 neurons), D1-MSNs in fear-conditioning session 4 (FC4, [ii], n = 180 neurons), D2-MSNs in FC1 ([iii], n = 107 neurons), and D2-MSNs in FC4 ([iv], n = 111 neurons.) Each time point is depicted as an arrow pointing in the direction of the next time point. The size of each arrow is proportional to the delay until the next time point (i.e., how fast the activity is moving along the trajectory with large arrows depicting more rapid changes). The pre-cue baseline period is colored light gray, the cue period is color coded (D2-MSN/FC1, red; D2-MSN/FC4, orange; D1-MSN/FC1, dark blue; D1-MSN/FC4, light blue), and the shock period is colored dark gray. As mice learn the cue-footshock contingency, D2 MSN cue responses, but not D1 MSN responses, become more variable.
(B) D2 MSNs were categorized based on observed activity patterns in the NAc during the initial fear-conditioning session (FC1) in the following categories: (i) response only to the cue, (ii) response only to the shock, and (iii) response both to the cue and shock.
(C) In D1 MSNs, most of the cells only responded to the shock during the initial fear-conditioning session (FC1).
(D) The D1 MSN cell recruitment to the cue and the shock was similar in the last fear-conditioning session (FC4), with a majority of cells responding only to the shock.
(E) In D2 MSNs, initially (on FC1) only a small percentage of cells responded to both the cue and shock.
(F) In FC4, a majority of D2 MSNs responded to both the cue and shock.
(G) D2 MSNs were recorded on the first session (FC1) and cells detected during this session were longitudinally co-registered with cells in the last session (FC4) based on activity during each session.
(H) Most of the cells that only responded to the cue in FC1 were not detected as active during the final fear-conditioning session (FC4, only 13% co-registered). The majority of D2 MSNs that responded to the shock (either shock alone, or both cue and shock) were re-recruited in FC4.
(I) Heatmaps showing cue responses for fear-conditioning session 1 and 4 ordered by the tune of response following cue presentation.
(J) Histogram of event numbers for each second of the cue period, superimposed on the Z scored averaged calcium responses. Event analysis showed that the number of D2 MSN events within the cue period increased with learning (chi square = 34.32, p < 0.0001) and the amplitude of those events became larger as well ([i] the whole cue period, unpaired t test, t718 = 4.26, p < 0.0001, n = 239–481 events). When clustered based on the timing of the response the peak event amplitude was larger in FC4 during the early segment ([ii] from the cue onset to 3 s; unpaired t test, t301 = 3.76, p = 0.0002, n = 78–225 events) but not during the middle ([iii] 3.5 s to 6.5 s, unpaired t test, t169 = 1.13, p = 0.26, n = 57–114 events) or the late ([iv] 7 s to the cue offset, unpaired t test, t191 = 1.33, p = 0.18, n = 73–120 events) segments of the cue period.
(K) The event onset was earlier in FC4 compared with FC1 (unpaired t test, t718 = 3.61, p = 0.0003, n = 239–481 events).
Data represented as mean ± SEM, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns, not significant. (fear-conditioning session 1 [FC1]; fear-conditioning session 4 [FC4]).
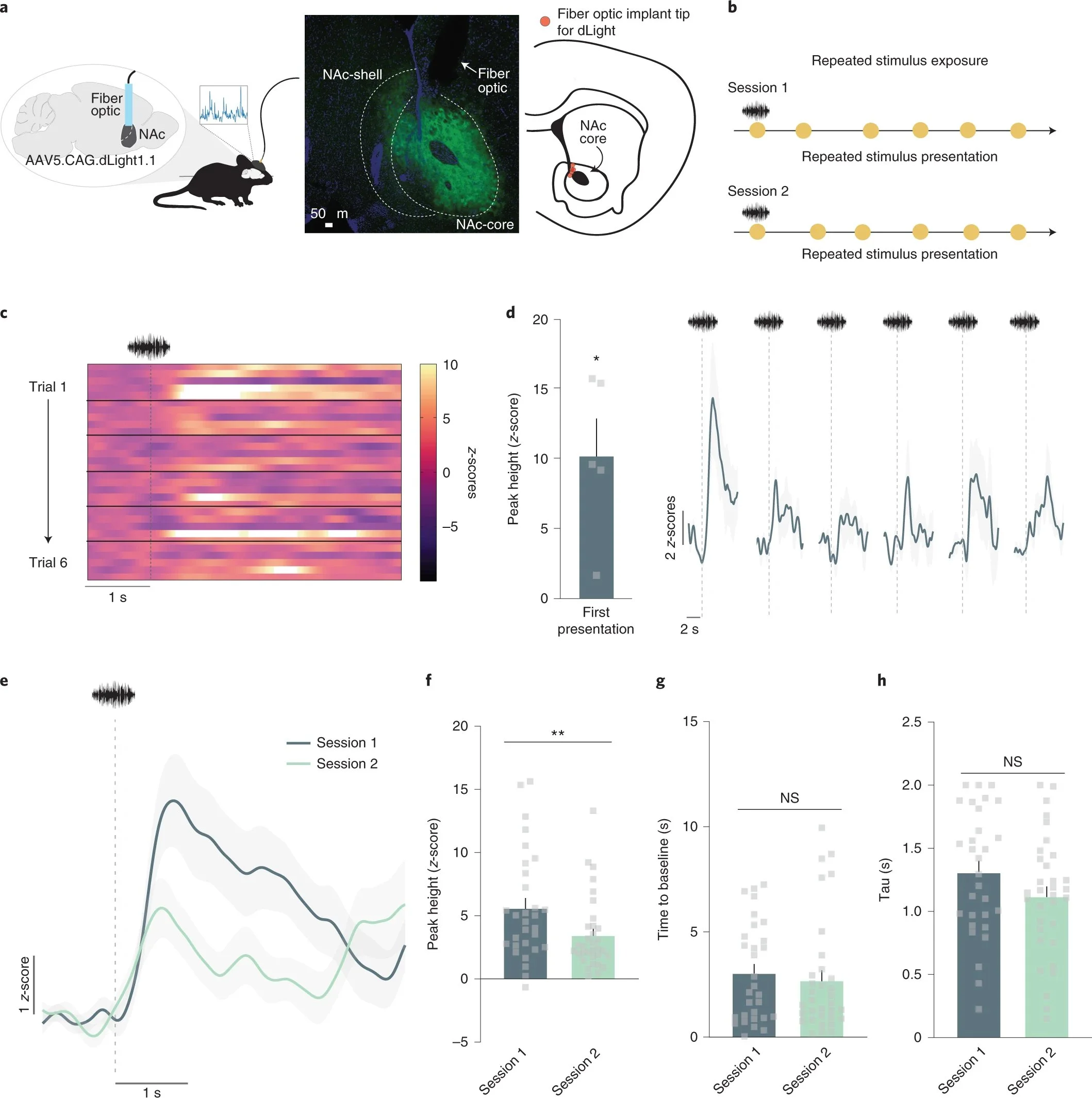
Dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens core mediates latent inhibition
Kutlu, Zachry, Melugin et al., Nature neuroscience, 2022
Studies investigating the neural mechanisms by which associations between cues and predicted outcomes control behavior often use associative learning frameworks to understand the neural control of behavior. These frameworks do not always account for the full range of effects that novelty can have on behavior and future associative learning. Here, in mice, we show that dopamine in the nucleus accumbens core is evoked by novel, neutral stimuli, and the trajectory of this response over time tracked habituation to these stimuli. Habituation to novel cues before associative learning reduced future associative learning, a phenomenon known as latent inhibition. Crucially, trial-by-trial dopamine response patterns tracked this phenomenon. Optogenetic manipulation of dopamine responses to the cue during the habituation period bidirectionally influenced future associative learning. Thus, dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens core has a causal role in novelty-based learning in a way that cannot be predicted based on purely associative factors.
Neutral stimuli elicit dopamine responses that decrease over repeated presentations. a, Mice (n = 5; 4 males, 1 female) received unilateral injections of the fluorescent dopamine sensor dLight1.1 in the NAc. A fiber optic cannula was placed directly above the injection site in the NAc core. Representative histology showing viral expression (green) restricted to the NAc core and schematic showing fiber optic placements (red) in experimental animals. b, Stimulus exposure paradigm. A white noise stimulus was pseudo-randomly presented at 85 dB for 6–7 presentations for two sessions. c, Heatmap showing the trial-by-trial dopamine response (z-scores) to the neutral stimulus from each mouse (n = 5 for each trial; 6 trials in total). d, Session 1 dopamine signal to repeated white noise presentations (6–7 presentations per animal). The first presentation of the neutral stimulus evoked a significant positive dopamine response (peak height for the first presentation; two-tailed independent sample t-test, t4 = 4.02, P = 0.01, n = 5 mice). e, Averaged dopamine responses to white noise presentations on session 1 versus session 2, showing that dopamine is reduced to neutral stimuli both within and across sessions. f, Peak dopamine response evoked by the white noise decreased from session 1 to session 2 (nested ANOVA F(1,57) = 7.26, P = 0.009, Session 1 n = 30 and Session 2 n = 33 stimulus presentations, n = 5 mice). g, The time for the dopamine signal to return to baseline in seconds did not significantly differ across sessions, suggesting that changes are driven by release, rather than clearance, mechanisms (nested ANOVA F(1,57) = 0.40, P = 0.5316). h, Tau is another measure of dopamine clearance and is defined by the time in seconds for the signal to return to two-thirds of peak height. This measure did not differ across sessions (nested ANOVA F(1,57) = 2.65, P = 0.1093). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS, not significant.
Cue pre-exposure leads to decreased dopamine responses and learning rate during subsequent fear learnings. Latent inhibition is a learning phenomenon where pre-exposure to a neutral stimulus reduces learning rates for that stimulus. a, Mice (n = 7; 5 males, 2 females) were pre-exposed to a stimulus (Pre-exposed CS+) for four sessions. b, The pre-exposed CS+ as well as a novel stimulus (CS+) were paired with a footshock for two sessions. A novel stimulus (CS−) was presented between each CS+ presentation and signaled the absence of the footshock. c, Freezing to the pre-exposed CS+, CS+ and CS− was measured (session 1; for session 2 see Extended Data Fig. 4). There was a main effect of pre-exposure (RM ANOVA F(2,12) = 11.50, P = 0.001) and freezing was higher to the CS+ than the pre-exposed CS+ (Tukey post-hoc P = 0.035). Freezing was increased to the CS+ as compared with the CS− (Tukey post-hoc P = 0.001). d, Percentage of time freezing across session 1. Freezing to the CS+ was greater than the pre-exposed CS+ (RM ANOVA main effect of pre-exposure F(1,8) = 9.76, P = 0.014, n = 5 mice). e, Trial-by-trial dopamine response (z-scores) to the pre-exposed CS+ and f, CS+ (c) (n = 5 mice for each trial; 6 trials in total). g, Averaged dopamine response over trials. ITI, averaged dopamine response during the time between CS+ presentations in the same session. h, Peak dopamine response to the CS+ was higher than the ITI responses (nested ANOVA F(2,113) = 2.51, P = 0.0006, Bonferroni post-hoc: CS+ versus pre-exposed CS+ P = 0.08; CS+ versus ITI P = 0.0002; n = 30 trials, n = 5 mice); pre-exposed CS+ did not differ from the ITI responses (Bonferroni post-hoc P = 0.32). i, Time for dopamine to return to baseline was slower for the CS+ compared with the pre-exposed CS+ (nested ANOVA F(2,113) = 19.70, P = 0.0001, Bonferroni post-hoc P < 0.0001; n = 30 trials, n = 5 mice) and the ITI dopamine response (Bonferroni post-hoc P < 0.0001). j, Tau (time for signal to return to two-thirds of peak) did not change between CS+ and pre-exposed CS+ (nested ANOVA F(2,113) = 2.13, P = 0.123, Bonferroni post-hoc: P > 0.05). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. RM, repeated measures ANOVA.
Dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core signals perceived saliency
Kutlu et al., Current biology, 2021
A large body of work has aimed to define the precise information encoded by dopaminergic projections innervating the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Prevailing models are based on reward prediction error (RPE) theory, in which dopamine updates associations between rewards and predictive cues by encoding perceived errors between predictions and outcomes. However, RPE cannot describe multiple phenomena to which dopamine is inextricably linked, such as behavior driven by aversive and neutral stimuli. We combined a series of behavioral tasks with direct, subsecond dopamine monitoring in the NAc of mice, machine learning, computational modeling, and optogenetic manipulations to describe behavior and related dopamine release patterns across multiple contingencies reinforced by differentially valenced outcomes. We show that dopamine release only conforms to RPE predictions in a subset of learning scenarios but fits valence-independent perceived saliency encoding across conditions. Here, we provide an extended, comprehensive framework for accumbal dopamine release in behavioral control.
Dopamine in the nucleus accumbens core does not track reward prediction error in negative reinforcement tasks. (A) Positive reinforcement task. (B) Dopamine was recorded via fiber photometry using dLight1.1. (C) Mice made more active than inactive responses during the post-training session (t6 = 3.18, p = 0.024; n = 6). (D and E) Heatmaps showing dopamine responses aligned around Sd,sucrose (left) and head entry (right) during (D) pre-training and (E) post-training. Each row represents a single Sd,sucrose presentation or head entry. (F and G) Averaged traces showing Sd,sucrose (F) and (G) head entry responses during pre- and post-training. (H) Dopamine increased to the Sd,sucrose (F1,153 = 10.79, p = 0.0013) and decreased to head entries over training (F1,75 = 11.17, p = 0.0013). (I) Negative reinforcement task. (J) Fiber photometry recording design. (K) Behavioral performance during negative reinforcement post-training session (t4 = 9.35, p < 0.001; n = 5). (L and M) Heatmaps of dopamine responses aligned around Sd,shock (left), footshock (center), and safety cue (right) during pre-training (L) and (M) post-training. (N–P) Dopamine traces to Sd,shock (N), (O) safety cue, and (P) footshock pre- and post-training. (Q) Dopamine response to Sd,shock (F1,96 = 1.52, p = 0.220), footshock (F1,127 = 4.00, p = 0.047), and safety cues (F1,95 = 15.46, p = 0.0002). Error bars represent ± S.E.M. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, ∗∗∗ p < 0.001.
Dopamine release signals perceived saliency (A) The Kutlu-Calipari-Schmajuk (KCS) model. The model has 4 core components. (1) Associative component: based on a Rescorla-Wagner prediction error term. (2) Attentional component: mismatch between predicted/unpredicted stimuli increases novelty, and in turn, attention to all stimuli in the environment. (3) Perceived saliency: novelty, attention, and the physical intensity of a stimulus determine perceived saliency. (4) Behavioral response component: perceived saliency is combined with associative strength to produce an outcome. (B–F) Experiments from Figure 4 were replotted to map onto model simulations. (B) Switching from positive reinforcement to punishment (denoted by dotted line) decreased simulated and actual nose pokes (r = 0.79, p < 0.0001; n = 5). (C) Perceived saliency of (gray) and dopamine responses to (blue) the cue similarly increased. (D–F) Dopamine response to the cue increased after a shock was introduced (t4 = 2.76, p = 0.025). KCS model simulations show that perceived saliency (E, R = 0.67, p < 0.0001) matches dopamine response patterns but prediction error does not (F, r = 0.092, p = 0.23).(G) Dopamine release was stimulated from terminals in the NAc core via optogenetics.(H) Dopamine release was evoked during fear conditioning to the cue on 25% of cue-shock pairings. (I) Increasing NAc core dopamine decreased freezing compared to EYFP controls (F1,20 = 17.84, p = 0.0004; ChR2-Tone + Stim versus EYFP-Tone + Stim, p ≤ 0.0001; ChR2-Tone + Stim versus ChR2-Tone only, p ≤ 0.0001; n = 5–6) and non-stimulated trials in the same animals (ChR2-Tone + Stim versus ChR2-Tone only, p = 0.0002). (J) KCS model simulations show that this behavior is predicted by increased perceived saliency. (K) NAc core dopamine release was evoked at the time of the omitted shock during extinction. (L) Dopamine stimulation prevented fear extinction in the ChR2 group compared to EYFP controls (F1,9 = 5.90, p = 0.038; last 4 trial block, t9 = 3.32, p = 0.0089; n = 5–6). (M) KCS simulations show that enhancing perceived saliency of the omitted shocks prevents extinction
Cocaine self-administration induces sex-dependent protein expression in the nucleus accumbens
Lopez and Johnson et al., Communications biology, 2021
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a chronic neuropsychiatric condition characterized by longlasting alterations in the neural circuitry regulating reward and motivation. Substantial work has focused on characterizing the molecular substrates that underlie these persistent changes in neural function and behavior. However, this work has overwhelmingly focused on male subjects, despite mounting clinical and preclinical evidence that females demonstrate dissimilar progression to SUD and responsivity to stimulant drugs of abuse, such as cocaine. Here, we show that sex is a critical biological variable that defines drug-induced plasticity in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Using quantitative mass spectrometry, we assessed the protein expression patterns induced by cocaine self-administration and demonstrated unique molecular profiles between males and females. We show that 1. Cocaine self-administration induces non-overlapping protein expression patterns in significantly regulated proteins in males and females and 2. Critically, cocaine-induced protein regulation differentially interacts with sex to eliminate basal sexual dimorphisms in the proteome. Finally, eliminating these baseline differences in the proteome is concomitant with the elimination of sex differences in behavior for non-drug rewards. Together, these data suggest that cocaine administration is capable of rewriting basal proteomic function and reward-associated behaviors.
Sexual dimorphisms in the proteomic landscape of the nucleus accumbens. Mass spectrometry was run on tissue from the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of male and female mice to determine the proteomic landscape. Differential expression between females as compared to males was assessed in control mice. (a) Volcano plot showing sexually dimorphic proteins in the nucleus accumbens from female versus male mice. Male and female accumbens proteomes diverge at key proteins—some associated with reward and drug response are noted. (b) Heat map of baseline sexually dimorphic proteins in the accumbens. Insets showing the top 15 proteins that were decreased (left) and increased (right) in females as compared to males. (c) In order to conduct Gene Ontology (GO) analysis protein names had to be converted to associated gene names. These conversions are available in Supplementary Data 1. Top GO terms in proteins downregulated in females (compared to males) and (d) proteins upregulated in females (compared to males). (e) Proteins making up the representative GO terms (top) downregulated in females (cytoplasmic part) and (bottom) upregulated in females (protein binding). (f) STRING analysis of predicted protein interaction network of proteins differentially expressed in males and females (g) within the protein binding cluster, and (h) neuron projection.
Cocaine self-administration regulates different proteins in males and females even when cocaine intake and self-administration behavior are not different. (a) A series of behavioral experiments were run to assess sex differences in motivation for cocaine self-administration in males and females. Schematic/timeline of self-administration. (b) Average responses for cocaine under escalating fixed ratio schedules in male and female mice. Male and female mice acquire and consume cocaine at comparable rates under FR1, 3, and 5 schedules of reinforcement. (c) A concentration–response curve was run across days with doses counterbalanced between animals (0.1, 0.3, 1, and 3 mg/kg). Data were plotted as a demand curve where consumption was plotted on the y-axis and price (in responses required to obtain 1 mg cocaine) was plotted on the x-axis. Curves were fit to determine consumption at a minimally constraining price (Q0) and the maximal price paid (Pmax) in males and females. Standardized Pmax (Q0 × Pmax) was calculated to allow for comparisons that are not influenced by the relative level of consumption and are comparable across groups. (d) Q0—plotted as mg/kg to control for body weight differences—was not significantly different between males and females. (e) Standardized Pmax was also not significantly different between males and females. (f) In a separate group of animals, mice were trained to self-administer cocaine (or saline for control) for 10 days, after which NAc tissue was collected and processed for mass spectrometry. Schematic of self-administration, tissue collection, and processing for mass spectrometry. (g) Male and female mice consumed cocaine at the same rate and (h) there were no differences in total cocaine consumption. (i) Proteins significantly altered by cocaine self-administration in the NAc of female mice. Dotted lines on the volcano plot denote the significance cut off. (j) Proteins significantly altered by cocaine self-administration in the NAc of male mice. (k) Volcano plot showing only the proteins that are significantly regulated in females and those same proteins in males. Most of the proteins significantly regulated in females are not regulated in males. (l) Volcano plot showing only the proteins that are significantly regulated in males and those same proteins from the female group.
An optimized procedure for robust volitional cocaine intake in mice
Lopez et al., Experimental and clinical Psychopharmacology, 2020
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a behavioral disorder characterized by volitional drug consumption. Mouse models of SUD allow for the use of molecular, genetic, and circuit level tools, providing enormous potential for defining the underlying mechanisms of this disorder. However, the relevance of results depends on the validity of the mouse models used. Self-administration models have long been the preferred preclinical model for SUD as they allow for volitional drug consumption, thus providing strong face validity. While previous work has defined the parameters that influence intravenous cocaine self-administration in other species - such as rats and primates - many of these parameters have not been explicitly assessed in mice. In a series of experiments, we show that commonly used mouse models of self-administration, where behavior is maintained on a fixed-ratio one schedule of reinforcement, show similar levels of responding in the presence and absence of drug delivery - demonstrating that it is impossible to determine when drug consumption is and is not volitional. To address these issues, we have developed a novel mouse self-administration procedure where animals do not need to be pre-trained on food and behavior is maintained on a variable ratio schedule of reinforcement. This procedure increases rates of reinforcement behavior, increases levels of drug intake, and results in clearer delineation between drug-reinforced mice and saline controls. Together, these data highlight a major issue with fixed-ratio models in mice that complicates subsequent analysis and provide a simple approach to minimize these confounds with escalating variable-ratio schedules of reinforcement.
New procedure for drug self-administration in mice that requires no food pre-training, shows robust self-administration, and increases drug intake. (A, left) Schematic for mouse intravenous cocaine self-administration. (A, right) Training and Self-administration schedule. (B) Active and inactive responses for cocaine (1mg/kg/inj) self-administration in mice on VR3 and VR5 schedules of reinforcement. Animals show a preference for active nose-poke compared to inactive that is schedule dependent. (C) Total cocaine infusions per session. (D) Active and inactive responses for saline in mice on VR3 and VR5 schedules of reinforcement. Mice do not show a preference for either the active or inactive nose-poke. (E) Total saline infusions per session. (F) Cumulative record of active and inactive responses across cocaine self-administration. (G) Cumulative record of cocaine infusions across cocaine self-administration. (H) Cumulative record of active and inactive responses across saline self-administration. (I) Cumulative record of saline infusions across saline self-administration. (J) Response rates on the active poke throughout training and self-administration. Cocaine animals demonstrate increased response rates on the active nose-poke throughout cocaine self-administration compared to saline controls. (K) Total active responses for saline and cocaine animals during VR3 and VR5. Cocaine animals respond more on active poke and increase responding under VR5 compared to saline controls. (L) Total inactive responses for saline and cocaine animals during VR3 and VR5. Cocaine animals respond less on the inactive poke compared to saline controls. (M) Cocaine animals demonstrate increased bias for active nose-poke during VR self-administration compared to saline controls. (N) Cocaine animals show increased bias during VR self-administration compared to saline controls.
A Novel Multidimensional Reinforcement Task in Mice Elucidates Sex-Specific Behavioral Strategies
Kutlu*, Zachry* et al., Neuropsychopharmacology, 2020
A large body of work has focused on understanding stimulus-driven behavior, sex differences in these processes, and the neural circuits underlying them. Many preclinical mouse models present rewarding or aversive stimuli in isolation, ignoring that ethologically, reward seeking requires the consideration of potential aversive outcomes. In addition, the context (or reinforcement schedule under) in which stimuli are encountered can engender different behavioral responses to the same stimulus. Thus, delineating neural control of behavior requires a dissociation between stimulus valence and stimulus-driven behavior. We developed the Multidimensional Cue Outcome Action Task (MCOAT) to dissociate motivated action from cue learning and valence in mice. First, mice acquire positive and negative reinforcement in the presence of discrete discriminative stimuli. Next, discriminative stimuli are presented concurrently allowing for parsing innate behavioral strategies based on reward seeking and avoidance. Lastly, responding in the face of punishment is assessed, thus examining how positive and negative outcomes are relatively valued. First, we identified sex-specific behavioral strategies, showing that females prioritize avoidance of negative outcomes over seeking positive, while males have the opposite strategy. Next, we show that chemogenetically inhibiting D1 medium spiny neurons (MSNs) in the nucleus accumbens-a population that has been linked to reward-driven behavior-reduces positive and increases negative reinforcement learning rates. Thus, D1 MSNs modulate stimulus processing, rather than motivated responses or the reinforcement process itself. Together, the MCOAT has broad utility for understanding complex behaviors as well as the definition of the discrete information encoded within cellular populations.
Females are biased towards avoiding aversive outcomes. Males and females demonstrate divergent rates of learning for positive and reinforcement; however, while females learn negative reinforcement at a slower rate they are biased towards avoiding aversive outcomes when they are presented concurrently with options to obtain rewards. Further, females demonstrate a bias for punishment avoidance and males demonstrate a bias for reward-seeking in the face of an aversive stimulus.
Chemogenetic inhibition of D1 MSNs in the NAc disrupts positive reinforcement and enhances negative reinforcement learning. a Representative image of viral expression of DREADDs (hM4Di—inhibitory) in the NAc core of D1-Cre mice. b Schematic of experimental design. c Chemogenetic inhibition of NAc D1 MSNs during positive reinforcement learning reduced active responses. d,e After the learning criterion was met, inhibition of D1 MSNs did not affect task performance. f D1 MSN inhibition enhanced acquisition of negative reinforcement. g D1 MSN inhibition did not affect post-training performance. e D1 MSN inhibition did not alter discrimination between sucrose and avoidance responses. h D1 MSN inhibition did not change response bias during conflict trials.
Cues play a critical role in estrous cycle-dependent enhancement of cocaine reinforcement
Johnson et al., Neuropsychopharmacology, 2019
While preclinical work has aimed to outline the neural mechanisms of drug addiction, it has overwhelmingly focused on male subjects. There has been a push in recent years to incorporate females into existing addiction models; however, males and females often have different behavioral strategies, making it important to not only include females, but to develop models that assess the factors that comprise female drug addiction. Traditional self-administration models often include light or tone cues that serve as discriminative stimuli and/or consequent stimuli, making it nearly impossible to disentangle the effects of cue learning, the cues themselves, and acute effects of psychostimulant drugs. To disentangle the interaction between drug-associated cues and the consummatory and appetitive responding driven by cocaine, we have developed a new behavioral procedure that combines Pavlovian-instrumental transfer with behavioral economic analysis. This task can be completed within a single session, allowing for studies looking at estrous cycle stage-dependent effects in intact cycling females, something that has been difficult in the past. In this study, we found no differences in self-administration across the estrous cycle in the absence of cues; however, when cues were introduced, the cues that acquired value during estrus—but not during diestrus or in males—increased motivation. Cues paired during estrus also increased c-fos expression to a greater extent in striatal regions, an effect that may underlie the observed increases in seeking induced by these cues, even weeks later. Together, these data suggest that fundamental differences in the motivational properties of psychostimulant drugs between males and females are complex and are driven primarily by the interaction between drug-associated stimuli and drug effects.
Figure 5. Cues are critical in the expression of sex differences in motivation. b Self-administration responses based on cycle stage on test day. There were no differences in responses across the dose-response curve. c No effect of cycle stage on the day of testing for motivation as measured by Pmax (left) or Q0 (right). d There was no change in responding over the dose-response curve or in Pmax (inset) in the presence of the diestrus paired cue when animals were in diestrus. e Similarly, there was no change in responding or in Pmax (inset) when cue was paired during diestrus and animal was tested in estrus. f No change in responding or in Pmax (inset) in the presence or absence of the cue in males. Cues that were paired in estrus increase motivation regardless of the cycle stage that the animal is in during testing. g Animals increased responding and Pmax (inset) in the presence of the estrus-paired cue during diestrus. h Similarly, estrus-paired cues increased responding and Pmax (inset) when animals were tested in estrus.
Figure 4. Mesolimbic and mesocortical activation patterns that underlie enhanced cue effects on motivation. c Number of c-fos+ and TH+ double-labeled cells in the VTA across groups. d c-fos+ and NeuN+ double-labeled cells in the infralimbic and prelimbic regions of the prefrontal cortex, *p < 0.05 compared to diestrus group (e) dorsolateral striatum, *p < 0.05 compared to male group (f) dorsomedial striatum, (g) NAc core, *p < 0.05 compared to male group and (i) NAc shell, *p < 0.05 compared to diestrus-paired group. h Correlation between number of lever presses and number of double-labeled c-fos+ and NeuN+ cells in the NAc core or (j) NAc shell.
Cocaine self-administration alters transcriptome-wide responses in the brain’s reward circuitry
Walker et al., Biological Psychiatry, 2018
Global changes in gene expression underlying circuit and behavioral dysregulation associated with cocaine addiction remain incompletely understood. Here, we show how a history of cocaine self-administration (SA) “re-programs” transcriptome-wide responses throughout the brain’s reward circuitry at baseline and in response to context and/or cocaine re-exposure after prolonged withdrawal (WD). We assigned male mice to one of six groups: saline/cocaine SA + 24 hr WD; or saline/cocaine SA + 30 d WD + an acute saline/cocaine challenge within the previous drug-paired context. RNA-sequencing was conducted on six interconnected brain reward regions. Using pattern analysis of gene expression and factor analysis of behavior, we identified genes that are strongly associated with addiction-related behaviors and uniquely altered by a history of cocaine SA. We then identified potential upstream regulators of these genes. We focused on three Patterns of gene expression that reflect responses to: a) acute cocaine, b) context re-exposure, and c) drug + context re-exposure. These Patterns revealed region-specific regulation of gene expression. Further analysis revealed that each of these gene expression Patterns correlated with an “Addiction Index”—a composite score of several addiction-like behaviors during cocaine SA—in a region-specific manner. CREB and nuclear receptor families were identified as key upstream regulators of genes associated with such behaviors. This comprehensive picture of transcriptome-wide regulation in the brain’s reward circuitry by cocaine SA and prolonged WD provides new insight into the molecular basis of cocaine addiction, which will guide future studies of the key molecular pathways involved.
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor controls neural and behavioral plasticity in response to cocaine
Calipari et al., Nature Communications, 2018
Cocaine addiction is characterized by dysfunction in reward-related brain circuits, leading to maladaptive motivation to seek and take the drug. There are currently no clinically available pharmacotherapies to treat cocaine addiction. Through a broad screen of innate immune mediators, we identify granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) as a potent mediator of cocaine-induced adaptations. Here we report that G-CSF potentiates cocaine-induced increases in neural activity in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and prefrontal cortex. In addition, G-CSF injections potentiate cocaine place preference and enhance motivation to selfadminister cocaine, while not affecting responses to natural rewards. Infusion of G-CSF neutralizing antibody into NAc blocks the ability of G-CSF to modulate cocaine’s behavioral effects, providing a direct link between central G-CSF action in NAc and cocaine reward. These results demonstrate that manipulating G-CSF is sufficient to alter the motivation for cocaine, but not natural rewards, providing a pharmacotherapeutic avenue to manipulate addictive behaviors without abuse potential.
Fig. 1 Serum multiplex analysis after self- and experimenter-administered cocaine in mice. a Timeline of experimenter-administered chronic cocaine injections. b Cocaine resulted in robust locomotor sensitization. c Timeline of cocaine self-administration in mice. d Average daily intake of cocaine across self-administration sessions. e Multiplex serum analysis of 32 chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors after experimenter- or self-administered cocaine. For each analyte, the heatmap depicts fold-change values compared to the respective saline group. Correlation heatmap of individual analyte levels with either locomotor sensitization (Day 10/Day 1) or daily intake of cocaine
Fig. 5 G-CSF levels are increased by the selective activation of mPFC to NAc projections. a Experimental design of projection-specific DREADD stimulation. Mice were injected with a retrograde traveling CAV2-Cre virus in the NAc and a Cre-dependent hM3Dq-DREADD virus in either the mPFC or the VTA to allow for the specific stimulation of either mPFC to NAc or VTA to NAc. b Csf3 (G-CSF) mRNA levels in the NAc were increased after mPFC to NAc stimulation. c Csf3r (G-CSFR) mRNA levels in the NAc were increased only after mPFC to NAc stimulation. d Peripheral G-CSF serum levels were not affected by stimulation.
Dopaminergic Dynamics underlying sex-specific cocaine reward
Calipari et al., Nature Communications, 2017
Although both males and females become addicted to cocaine, females transition to addiction faster and experience greater difficulties remaining abstinent. We demonstrate an oestrous cycle-dependent mechanism controlling increased cocaine reward in females. During oestrus, ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine neuron activity is enhanced and drives post translational modifications at the dopamine transporter (DAT) to increase the ability of cocaine to inhibit its function, an effect mediated by estradiol. Female mice conditioned to associate cocaine with contextual cues during oestrus have enhanced mesolimbic responses to these cues in the absence of drug. Using chemogenetic approaches, we increase VTA activity to mechanistically link oestrous cycle-dependent enhancement of VTA firing to enhanced cocaine affinity at DAT and subsequent reward processing. These data have implications for sexual dimorphism in addiction vulnerability and define a mechanism by which cellular activity results in protein alterations that contribute to dysfunctional learning and reward processing.
Proposed schematic highlighting a potential mechanism for the activity-dependent changes in reward processing that occur during oestrus. (1) The VTA to NAc pathway comprises dopaminergic neurons (purple) and other neuronal subpopulations (grey). (2) Dopamine neuron firing is enhanced during oestrus. (3) The increased activity of this pathway leads to downstream ERK activation and concomitant phosphorylation of Thr53 (blue) on DAT. (4) These changes in DAT lead to alterations in cocaine affinity, whereby cocaine is more able to bind to DAT and increase extracellular dopamine levels. This increased cocaine binding leads to increased dopamine levels in the NAc. (5) In vivo this drives increased associations between cocaine and contextual cues, which leads to enhanced cocaine CPP due to differences in the perceived rewarding value of cocaine.
Figure 5. Download manuscript PDF below.
In vivo imaging identifies temporal signature of D1 and D2 Medium Spiny Neurons in cocaine reward
Calipari et al, Proceedings of the national academy of science, USA, 2016
The reinforcing and rewarding properties of cocaine are attributed to its ability to increase dopaminergic transmission in nucleus accumbens (NAc). This action reinforces drug taking and seeking and leads to potent and long-lasting associations between the rewarding effects of the drug and the cues associated with its availability. The inability to extinguish these associations is a key factor contributing to relapse. Dopamine produces these effects by controlling the activity of two subpopulations of NAc medium spiny neurons (MSNs) that are defined by their predominant expression of either dopamine D1 or D2 receptors. Previous work has demonstrated that optogenetically stimulating D1 MSNs promotes reward, whereas stimulating D2 MSNs produces aversion. However, we still lack a clear understanding of how the endogenous activity of these cell types is affected by cocaine and encodes information that drives drug-associated behaviors. Using fiber photometry calcium imaging we define D1 MSNs as the specific population of cells in NAc that encodes information about drug associations and elucidate the temporal profile with which D1 activity is increased to drive drug seeking in response to contextual cues. Chronic cocaine exposure dysregulates these D1 signals to both prevent extinction and facilitate reinstatement of drug seeking to drive relapse. Directly manipulating these D1 signals using designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs prevents contextual associations. Together, these data elucidate the responses of D1- and D2-type MSNs in NAc to acute cocaine and during the formation of context-reward associations and define how prior cocaine exposure selectively dysregulates D1 signaling to drive relapse.
This work outlined the temporally signature of D1 and D2 medium spiny neuron encoding of reward information and how it is dysregulated by cocaine exposure to drive addictive behaviors.
Figure 2. Download manuscript PDF below.